Dance and AI
Al ROBOLAB @University of Luxembourg | N. Shojaee, B. Antico |2022


Al ROBOLAB @University of Luxembourg | N. Shojaee, B. Antico |2022


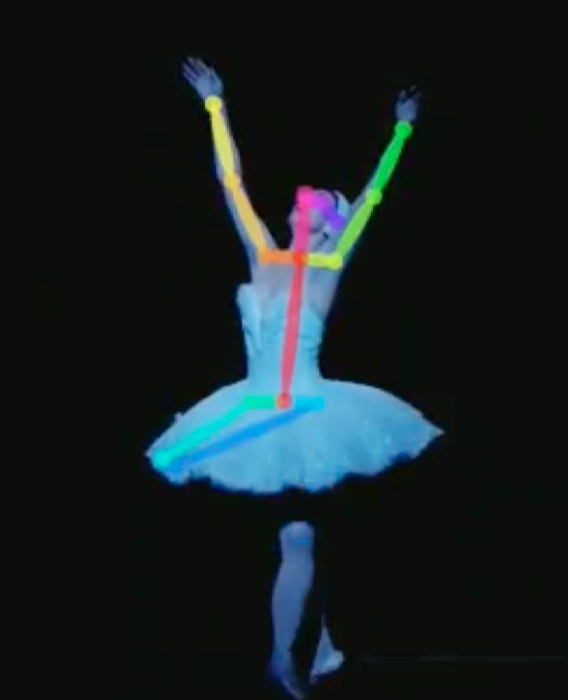
For this exhibition in 2022, we trained an AI program to listen to music and generate dance moves to accompany this music. These two videos give you two examples of dance moves generated by our AI program to two different dance styles: ballet and tango.
These videos show the results of an artificial intelligence that was trained on 71 hours of footage of dance clips with music. The dance poses are defined by 14 key points (arm and leg joints, shoulders, …) forming a skeleton representing the dance moves. The AI chooses a series of dance moves that best fit the music, based on the training data the program has learned on.
During the project, many challenges came up to make the AI understand dance moves and to make them fit to the music. Especially for the more complex dance moves, the AI had trouble to map the skeleton to the dance moves. Have a look at the following video on the left showing both a training video of a ballet dancer and the output of the AI alternatively. The right shows two images of challenging dance poses.

The left leg of the dancer is lifted behind her body and thus invisible, making it impossible to correctly define the skeleton.
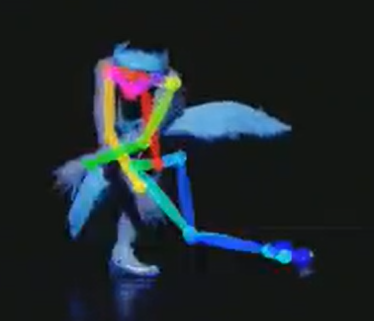
A more complex pose as seen above poses problems for the AI to correctly connect the skeleton’s key points to the dancer.
A follow-up idea to these automated dances we had was to make a semi-humanoid robot dance. Pepper is the first social semi-humanoid robot manufactured by SoftBank Robotics, that is able to recognize faces and basic human emotions. Pepper was optimized for human interaction and is able to engage with people through conversation and its touch screen. Pepper’s physical and interactive features raised our interest to design a basic ballet dance sequence for it and experiment human-robot interaction through dance. Have a look at dance choreographies using the Pepper robot in the following video.
Copyright © Université du Luxembourg 2025. All rights reserved.